
|  |  |  Editorials | Environmental | March 2009 Editorials | Environmental | March 2009  
Catastrophic Fall in 2009 Global Food Production
 Eric deCarbonnel - Market Skeptics Eric deCarbonnel - Market Skeptics
go to original

After reading about the droughts in two major agricultural countries, China and Argentina, I decided to research the extent other food producing nations were also experiencing droughts. This project ended up taking a lot longer than I thought. 2009 looks to be a humanitarian disaster around much of the world.

To understand the depth of the food catastrophe that faces the world this year, consider the graphic below depicting countries by USD value of their agricultural output, as of 2006.

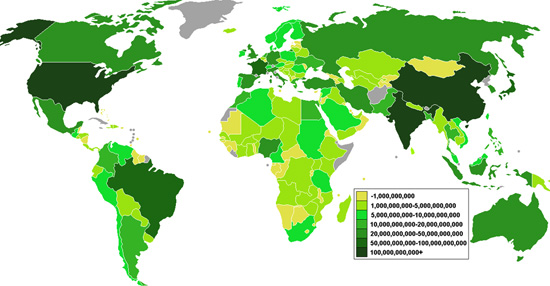

Now, consider the same graphic with the countries experiencing droughts highlighted.

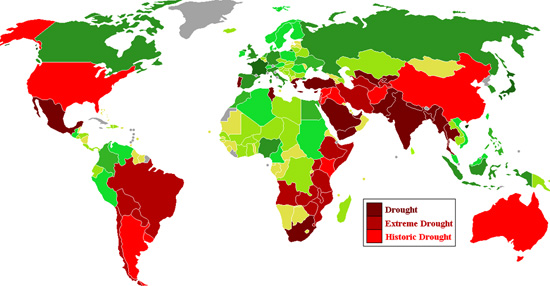

The countries that make up two thirds of the world’s agricultural output are experiencing drought conditions. Whether you watch a video of the drought in China, Australia, Africa, South America, or the US, the scene will be the same: misery, ruined crop, and dying cattle.

China

The drought in Northern China, the worst in 50 years, is worsening, and summer harvest is now threatened. The area of affected crops has expanded to 161 million mu (was 141 million last week), and 4.37 million people and 2.1 million livestock are facing drinking water shortage. The scarcity of rain in some parts of the north and central provinces is the worst in recorded history.

The drought which started in November threatens over half the wheat crop in eight provinces - Hebei, Shanxi, Anhui, Jiangsu, Henan, Shandong, Shaanxi and Gansu.

Henan: China's largest crop producing province, Henan, has issued the highest-level drought warning. Henan has received an average rainfall of 10.5 millimeters since November 2008, almost 80 percent less than in the same period in the previous years. The Henan drought, which began in November, is the most severe since 1951.

Anhui: Anhui Province issued a red drought alert, with more than 60 percent of the crops north of the Huaihe River plagued by a major drought.

Shanxi: Shanxi Province was put on orange drought alert on Jan. 21, with one million people and 160,000 heads of livestock are facing water shortage.

Jiangsu: Jiangsu province has already lost over one fifth of the wheat crops affected by drought. Local agricultural departments are diverting water from nearby rivers in an emergency effort to save the rest.

Hebei: Over 100 million cubic meters of water has been channeled in from outside the province to fight Hebei’s drought.

Shaanxi: 1.34 million acres of crops across the bone-dry Shanxi province are affected by the worsening drought.

Shandong: Since last November, Shandong province has experienced 73 percent less rain than the same period in previous years, with little rainfall forecast for the future.

Relief efforts are under way. The Chinese government has allocated 86.7 billion yuan (about $12.69 billion) to drought-hit areas. Authorities have also resorted to cloud-seeding, and some areas received a sprinkling of rain after clouds were hit with 2,392 rockets and 409 cannon shells loaded with chemicals. However, there is a limit to what can be done in the face of such widespread water shortage.

As I have previously written, China is facing hyperinflation, and this record drought will make things worse. China produces 18% of the world's grain each year.

Australia

Australia has been experiencing an unrelenting drought since 2004, and 41 percent of Australia's agriculture continues to suffer from the worst drought in 117 years of record-keeping. The drought has been so severe that rivers stopped flowing, lakes turned toxic, and farmers abandoned their land in frustration:

A) The Murray River stopped flowing at its terminal point, and its mouth has closed up.
B) Australia’s lower lakes are evaporating, and they are now a meter (3.2 feet) below sea level. If these lakes evaporate any further, the soil and the mud system below the water is going to be exposed to the air. The mud will then acidify, releasing sulfuric acid and a whole range of heavy metals. After this occurs, those lower lake systems will essentially become a toxic swamp which will never be able to be recovered. The Australian government's only options to prevent this are to allow salt water in, creating a dead sea, or to pray for rain.

For some reason, the debate over climate change is essentially over in Australia.

The United States

California: California is facing its worst drought in recorded history. The drought is predicted to be the most severe in modern times, worse than those in 1977 and 1991. Thousands of acres of row crops already have been fallowed, with more to follow. The snowpack in the Northern Sierra, home to some of the state's most important reservoirs, proved to be just 49 percent of average. Water agencies throughout the state are scrambling to adopt conservation mandates.

Texas: The Texan drought is reaching historic proportion. Dry conditions near Austin and San Antonio have been exceeded only once before—the drought of 1917-18. 88 percent of Texas is experiencing abnormally dry conditions, and 18 percent of the state is in either extreme or exceptional drought conditions. The drought areas have been expanding almost every month. Conditions in Texas are so bad cattle are keeling over in parched pastures and dying. Lack of rainfall has left pastures barren, and cattle producers have resorted to feeding animals hay. Irreversible damage has been done to winter wheat crops in Texas. Both short and long-term forecasts don't call for much rain at all, which means the Texas drought is set to get worse.

Augusta Region (Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina): The Augusta region has been suffering from a worsening two year drought. Augusta’s rainfall deficit is already approaching 2 inches so far in 2009, with January being the driest since 1989.

Florida: Florida has been hard hit by winter drought, damaging crops, and half of state is in some level of a drought.

La Niña likely to make matters worse

Enough water a couple of degrees cooler than normal has accumulated in the eastern part of the Pacific to create a La Niña, a weather pattern expected to linger until at least the spring. La Niña generally means dry weather for Southern states, which is exactly what the US doesn’t need right now.

South America

Argentina: The worst drought in half a century has turned Argentina's once-fertile soil to dust and pushed the country into a state of emergency. Cow carcasses litter the prairie fields, and sun-scorched soy plants wither under the South American summer sun. Argentina's food production is set to go down a minimum of 50 percent, maybe more. The country's wheat yield for 2009 will be 8.7 million metric tons, down from 16.3 million in 2008. Concern with domestic shortages (domestic wheat consumption being approximately 6.7 million metric ton), Argentina has granted no new export applications since mid January.

Brazil: Brazil has cut its outlook for the crops and will do so again after assessing damage to plants from desiccation in drought-stricken regions. Brazil is the world's second-biggest exporter of soybeans and third-largest for corn.

Brazil's numbers for corn harvesting:

Harvested in 2008: 58.7 million tons
January 8 forecast: 52.3 million tons
February 6 forecast: 50.3 metric tons (optimistic)
Harvested in 2009: ???

Paraguay: Severe drought affecting Paraguay's economy has pushed the government to declare agricultural emergency. Crops that have direct impact on cattle food are ruined, and the soy plantations have been almost totally lost in some areas.

Uruguay: Uruguay declared an "agriculture emergency" last month, due to the worst drought in decades which is threatening crops, livestock and the provision of fresh produce. The a worsening drought is pushing up food and beverage costs causing Uruguay's consumer prices to rise at the fastest annual pace in more than four years in January.

Bolivia: There hasn’t been a drop of rain in Bolivia in nearly a year. Cattle dying, crops ruined, etc…

Chile: The severe drought affecting Chile has caused an agricultural emergency in 50 rural districts, and large sectors of the economy are concerned about possible electricity rationing in March. The countries woes stem from the "La Niña" climate phenomenon which has over half of Chile dangling by a thread: persistently cold water in the Pacific ocean along with high atmospheric pressure are preventing rain-bearing fronts from entering central and southern areas of the country. As a result, the water levels at hydroelectric dams and other reservoirs are at all-time lows.

Horn of Africa

Africa faces food shortages and famine. Food production across the Horn of Africa has suffered because of the lack of rainfall. Also, half the agricultural soil has lost nutrients necessary to grow plant, and the declining soil fertility across Africa is exacerbating drought related crop losses.

Kenya: Kenya is the worst hit nation in the region, having been without rainfall for 18 months. Kenya needs to import food to bridge a shortfall and keep 10 million of its people from starvation. Kenya’s drought suffering neighbors will be of little help.

Tanzania: A poor harvest due to drought has prompted Tanzania to stop issuing food export permits. Tanzania has also intensified security at the border posts to monitor and prevent the export of food. There are 240,000 people in need of immediate relief food in Tanzania.

Burundi: Crops in the north of Burundi have withered, leaving the tiny East African country facing a severe food shortage

Uganda: Severe drought in northeastern Uganda's Karamoja region has the left the country on the brink of a humanitarian catastrophe. The dry conditions and acute food shortages, which have left Karamoja near starvation, are unlikely to improve before October when the next harvest is due.

South Africa: South Africa faces a potential crop shortage after wheat farmers in the eastern part of the Free State grain belt said they were likely to produce their lowest crop in 30 years this year. South Africans are "extremely angry" that food prices continue to rise.

Other African nations suffering from drought in 2009 are: Malawi, Zambia, Swaziland, Somalia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Tunisia, Angola, and Ethiopia.

Middle East and Central Asia

The Middle East and Central Asia are suffering from the worst droughts in recent history, and food grain production has dropped to some of the lowest levels in decades. Total wheat production in the wider drought-affected region is currently estimated to have declined by at least 22 percent in 2009. Owing to the drought's severity and region-wide scope, irrigation supplies from reservoirs, rivers, and groundwater have been critically reduced. Major reservoirs in Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Syria are all at low levels requiring restrictions on usage. Given the severity of crop losses in the region, a major shortage of planting seed for the 2010 crop is expected.

Iraq: In Iraq during the winter grain growing period, there was essentially no measurable rainfall in many regions, and large swaths of rain-fed fields across northern Iraq simply went unplanted. These primarily rain-fed regions in northern Iraq are described as an agricultural disaster area this year, with wheat production falling 80-98 percent from normal levels. The USDA estimates total wheat production in Iraq in 2009 at 1.3 million tons, down 45 percent from last year.

Syria: Syria is experienced its worst drought in the past 18 years, and the USDA estimates total wheat production in Syria in 2009 at 2.0 million tons, down 50 percent from last year. Last summer, the taps ran dry in many neighborhoods of Damascus and residents of the capital city were forced to buy water on the black market. The severe lack of rain this winter has exacerbated the problem.

Afghanistan: Lack of rainfall has led Afghanistan to the worst drought conditions in the past 10 years. The USDA estimates 2008/09 wheat production in Afghanistan at 1.5 million tons, down 2.3 million or 60 percent from last year. Afghanistan normally produces 3.5-4.0 million tons of wheat annually.

Jordan: Jordan's persistent drought has grown worse, with almost no rain falling on the kingdom this year. The Jordanian government has stopped pumping water to farms to preserve the water for drinking purposes.

Other Middle Eastern and Central Asian nations suffering from drought in 2009 are: The Palestinian Territories, Lebanon, Israel, Bangladesh, Myanmar, India, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Thailand, Nepal, Pakistan, Turkey, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Cyprus, and Iran.

Lack of credit will worsen food shortage

A lack of credit for farmers curbed their ability to buy seeds and fertilizers in 2008/2009 and will limit production around the world. The effects of droughts worldwide will also be amplified by the smaller amount of seeds and fertilizers used to grow crops.

Low commodity prices will worsen food shortage

The low prices at the end of 2008 discouraged the planting of new crops in 2009. In Kansas for example, farmers seeded nine million acres, the smallest planting for half a century. Wheat plantings this year are down about 4 million acres across the US and about 1.1 million acres in Canada. So even discounting drought related losses, the US, Canada, and other food producing nations are facing lower agricultural output in 2009.

Europe will not make up for the food shortfall

Europe, the only big agricultural region relatively unaffected by drought, is set for a big drop in food production. Due to the combination of a late plantings, poorer soil conditions, reduced inputs, and light rainfall, Europe’s agricultural output is likely to fall by 10 to 15 percent.

Stocks of foodstuff are dangerously low

Low stocks of foodstuff make the world’s falling agriculture output particularly worrisome. The combined averaged of the ending stock levels of the major trading countries of Australia, Canada, United States, and the European Union have been declining steadily in the last few years:

2002-2005: 47.4 million tons
2007: 37.6 million tons
2008: 27.4 million tons

These inventory numbers are dangerously low, especially considering the horrifying possibility that China’s 60 million tons of grain reserves doesn't actually exists.

Global food Catastrophe

The world is heading for a drop in agricultural production of 20 to 40 percent, depending on the severity and length of the current global droughts. Food producing nations are imposing food export restrictions. Food prices will soar, and, in poor countries with food deficits, millions will starve.

The deflation debate should end now

The droughts plaguing the world’s biggest agricultural regions should end the debate about deflation in 2009. The demand for agricultural commodities is relatively immune to developments in the business cycles (at least compared to that of energy or base metals), and, with a 20 to 40 percent decline in world production, already rising food prices are headed significantly higher.

In fact, agricultural commodities NEED to head higher and soon, to prevent even greater food shortages and famine. The price of wheat, corn, soybeans, etc must rise to a level which encourages the planting of every available acre with the best possible fertilizers. Otherwise, if food prices stay at their current levels, production will continue to fall, sentencing millions more to starvation.

Competitive currency appreciation

Some observers are anticipating “competitive currency devaluations” in addition to deflation for 2009 (nations devalue their currencies to help their export sector). The coming global food shortage makes this highly unlikely. Depreciating their currency in the current environment will produce the unwanted consequence of boosting exports—of food. Even with export restrictions like those in China, currency depreciation would cause the outflow of significant quantities of grain via the black market.

Instead of “competitive currency devaluations”, spiking food prices will likely cause competitive currency appreciation in 2009. Foreign exchange reserves exist for just this type of emergency. Central banks around the world will lower domestic food prices by either directly selling off their reserves to appreciate their currencies or by using them to purchase grain on the world market.

Appreciating a currency is the fastest way to control food inflation. A more valuable currency allows a nation to monopolize more global resources (ie: the overvalued dollar allows the US to consume 25% of the world's oil despite having only 4% of the world's population). If China were to selloff its US reserves, its enormous population would start sucking up the world's food supply like the US has been doing with oil.

On the flip side, when a nation appreciates its currency and starts consuming more of the world’s resources, it leaves less for everyone else. So when china appreciates the yuan, food shortages worldwide will increase and prices everywhere else will jump upwards. As there is nothing that breeds social unrest like soaring food prices, nations around the world, from Russia, to the EU, to Saudi Arabia, to India, will sell off their foreign reserves to appreciate their currencies and reduce the cost of food imports. In response to this, China will sell even more of its reserves and so on. That is competitive currency appreciation.

When faced with competitive currency appreciation, you do NOT want to be the world’s reserve currency. The dollar is likely to do very poorly as central banks liquidate trillions in US holdings to buy food and appreciate their currencies. |

 |
|  |



